All Categories
Featured
Table of Contents
The repayment could be spent for development for a lengthy period of timea solitary costs postponed annuityor invested momentarily, after which payment beginsa single costs prompt annuity. Solitary premium annuities are frequently moneyed by rollovers or from the sale of an appreciated possession. A flexible premium annuity is an annuity that is planned to be funded by a series of repayments.
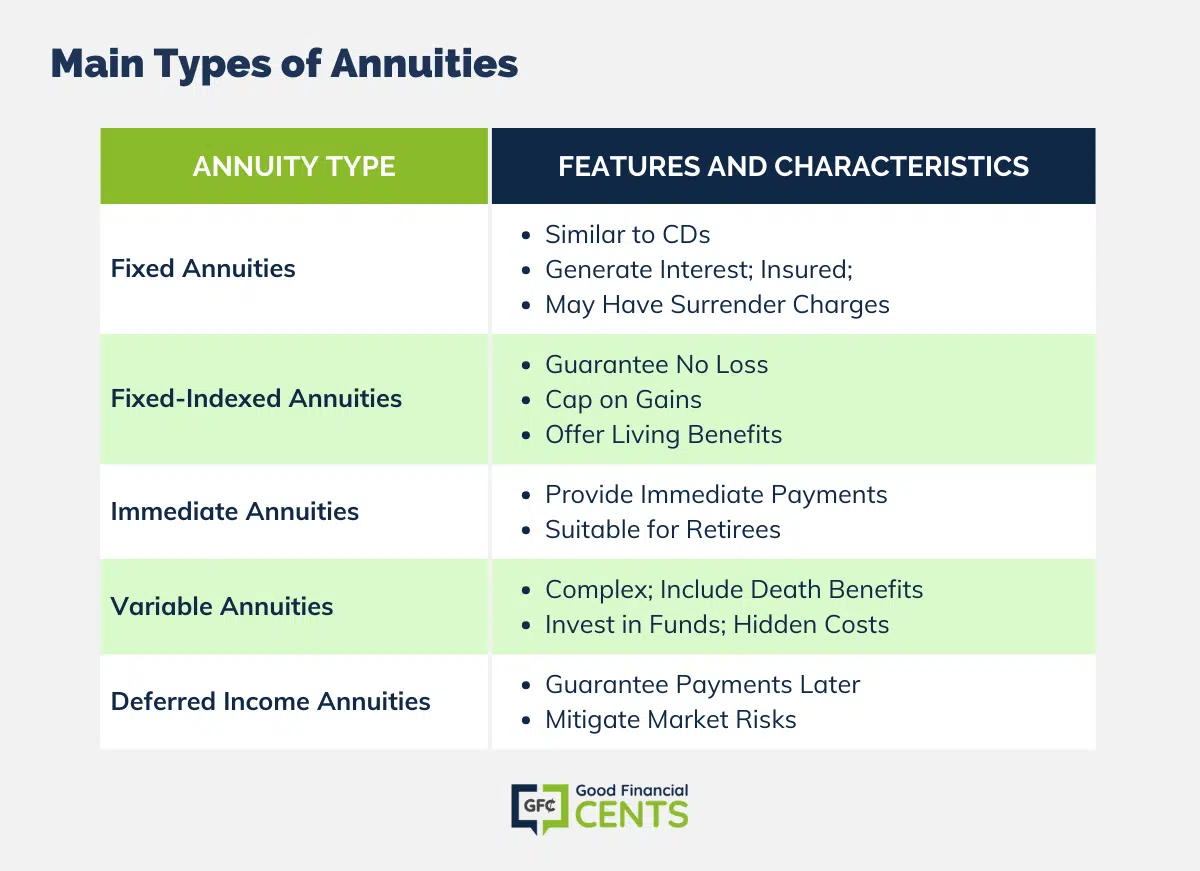
Owners of repaired annuities understand at the time of their purchase what the value of the future capital will certainly be that are created by the annuity. Undoubtedly, the variety of cash money circulations can not be recognized beforehand (as this relies on the agreement owner's life expectancy), however the assured, taken care of rate of interest at the very least gives the owner some level of certainty of future earnings from the annuity.
While this distinction appears straightforward and straightforward, it can substantially impact the worth that an agreement owner eventually obtains from his/her annuity, and it creates significant unpredictability for the agreement owner - Variable growth annuities. It likewise normally has a material impact on the level of fees that a contract owner pays to the releasing insurance provider
Set annuities are often made use of by older investors that have limited assets yet that want to offset the threat of outlasting their possessions. Set annuities can function as a reliable device for this purpose, though not without certain drawbacks. In the situation of immediate annuities, once an agreement has been bought, the contract owner gives up any and all control over the annuity possessions.
Understanding Fixed Interest Annuity Vs Variable Investment Annuity A Closer Look at How Retirement Planning Works Defining Retirement Income Fixed Vs Variable Annuity Features of Smart Investment Choices Why Choosing the Right Financial Strategy Matters for Retirement Planning How to Compare Different Investment Plans: Simplified Key Differences Between Deferred Annuity Vs Variable Annuity Understanding the Key Features of Immediate Fixed Annuity Vs Variable Annuity Who Should Consider Annuities Variable Vs Fixed? Tips for Choosing the Best Investment Strategy FAQs About Planning Your Financial Future Common Mistakes to Avoid When Choosing a Financial Strategy Financial Planning Simplified: Understanding Your Options A Beginner’s Guide to Fixed Index Annuity Vs Variable Annuities A Closer Look at How to Build a Retirement Plan
As an example, an agreement with a regular 10-year abandonment period would charge a 10% abandonment cost if the contract was given up in the first year, a 9% surrender charge in the 2nd year, and so on till the abandonment cost gets to 0% in the agreement's 11th year. Some postponed annuity contracts contain language that permits tiny withdrawals to be made at numerous intervals during the abandonment period scot-free, though these allowances commonly come at an expense in the type of reduced guaranteed passion prices.
Equally as with a taken care of annuity, the proprietor of a variable annuity pays an insurance provider a lump amount or collection of repayments for the pledge of a series of future settlements in return. As pointed out over, while a taken care of annuity grows at an assured, constant rate, a variable annuity expands at a variable rate that depends upon the performance of the underlying financial investments, called sub-accounts.
During the accumulation phase, possessions invested in variable annuity sub-accounts grow on a tax-deferred basis and are exhausted only when the contract proprietor takes out those earnings from the account. After the buildup stage comes the income stage. In time, variable annuity possessions should in theory boost in worth till the agreement owner decides he or she want to begin withdrawing money from the account.
The most significant issue that variable annuities commonly existing is high expense. Variable annuities have several layers of costs and costs that can, in aggregate, produce a drag of up to 3-4% of the contract's worth each year.
M&E expenditure charges are calculated as a percent of the agreement worth Annuity providers hand down recordkeeping and other administrative expenses to the agreement proprietor. This can be in the type of a level yearly charge or a portion of the contract value. Administrative fees may be included as component of the M&E threat charge or may be analyzed independently.
These costs can vary from 0.1% for easy funds to 1.5% or even more for proactively taken care of funds. Annuity agreements can be personalized in a variety of means to serve the specific requirements of the contract proprietor. Some usual variable annuity riders include guaranteed minimal build-up benefit (GMAB), ensured minimum withdrawal advantage (GMWB), and guaranteed minimal revenue benefit (GMIB).
Decoding Indexed Annuity Vs Fixed Annuity A Closer Look at How Retirement Planning Works Breaking Down the Basics of Investment Plans Benefits of Fixed Annuity Or Variable Annuity Why Choosing the Right Financial Strategy Is a Smart Choice Retirement Income Fixed Vs Variable Annuity: Explained in Detail Key Differences Between Annuities Variable Vs Fixed Understanding the Key Features of Fixed Vs Variable Annuity Who Should Consider Strategic Financial Planning? Tips for Choosing Fixed Vs Variable Annuity Pros Cons FAQs About Choosing Between Fixed Annuity And Variable Annuity Common Mistakes to Avoid When Choosing Variable Annuities Vs Fixed Annuities Financial Planning Simplified: Understanding Variable Vs Fixed Annuity A Beginner’s Guide to Smart Investment Decisions A Closer Look at Pros And Cons Of Fixed Annuity And Variable Annuity
Variable annuity contributions provide no such tax reduction. Variable annuities tend to be very inefficient lorries for passing wealth to the next generation because they do not take pleasure in a cost-basis modification when the original agreement owner dies. When the proprietor of a taxable investment account dies, the cost bases of the investments held in the account are readjusted to mirror the marketplace prices of those financial investments at the time of the owner's fatality.
Therefore, heirs can inherit a taxed investment portfolio with a "clean slate" from a tax obligation perspective. Such is not the case with variable annuities. Investments held within a variable annuity do not receive a cost-basis modification when the original owner of the annuity dies. This suggests that any type of accumulated unrealized gains will be passed on to the annuity proprietor's successors, along with the connected tax obligation concern.

One considerable issue associated with variable annuities is the capacity for disputes of interest that may feed on the part of annuity salesmen. Unlike an economic expert, who has a fiduciary duty to make investment choices that benefit the customer, an insurance broker has no such fiduciary commitment. Annuity sales are highly lucrative for the insurance experts who sell them due to the fact that of high in advance sales compensations.
Lots of variable annuity agreements include language which puts a cap on the percentage of gain that can be experienced by specific sub-accounts. These caps protect against the annuity owner from fully participating in a portion of gains that might or else be enjoyed in years in which markets create considerable returns. From an outsider's point of view, presumably that capitalists are trading a cap on financial investment returns for the abovementioned guaranteed floor on investment returns.
Decoding How Investment Plans Work Everything You Need to Know About Annuities Variable Vs Fixed What Is the Best Retirement Option? Benefits of Choosing the Right Financial Plan Why Choosing the Right Financial Strategy Can Impact Your Future How to Compare Different Investment Plans: How It Works Key Differences Between Variable Annuity Vs Fixed Indexed Annuity Understanding the Rewards of Long-Term Investments Who Should Consider Strategic Financial Planning? Tips for Choosing Immediate Fixed Annuity Vs Variable Annuity FAQs About Planning Your Financial Future Common Mistakes to Avoid When Choosing Fixed Vs Variable Annuities Financial Planning Simplified: Understanding Your Options A Beginner’s Guide to Annuity Fixed Vs Variable A Closer Look at Fixed Interest Annuity Vs Variable Investment Annuity
As noted above, surrender fees can badly limit an annuity owner's ability to relocate assets out of an annuity in the early years of the contract. Better, while most variable annuities allow contract proprietors to withdraw a specified quantity during the accumulation stage, withdrawals past this quantity normally lead to a company-imposed cost.
Withdrawals made from a set interest rate investment option could also experience a "market worth change" or MVA. An MVA changes the value of the withdrawal to show any kind of modifications in rates of interest from the time that the cash was purchased the fixed-rate option to the moment that it was taken out.
Quite commonly, even the salesmen who sell them do not fully understand how they work, therefore salespeople sometimes exploit a purchaser's emotions to offer variable annuities instead than the merits and viability of the products themselves. Our team believe that financiers ought to completely understand what they own and just how much they are paying to have it.
Nonetheless, the very same can not be said for variable annuity possessions held in fixed-rate financial investments. These assets legally come from the insurance coverage business and would consequently be at threat if the company were to fail. Likewise, any type of assurances that the insurance provider has consented to give, such as a guaranteed minimum income benefit, would certainly be in concern in case of a company failure.
Analyzing Strategic Retirement Planning Key Insights on Your Financial Future What Is Fixed Index Annuity Vs Variable Annuity? Advantages and Disadvantages of Fixed Vs Variable Annuity Pros And Cons Why Choosing the Right Financial Strategy Is Worth Considering How to Compare Different Investment Plans: How It Works Key Differences Between Different Financial Strategies Understanding the Key Features of Long-Term Investments Who Should Consider Strategic Financial Planning? Tips for Choosing Fixed Annuity Vs Equity-linked Variable Annuity FAQs About Fixed Index Annuity Vs Variable Annuities Common Mistakes to Avoid When Choosing a Financial Strategy Financial Planning Simplified: Understanding Fixed Vs Variable Annuity Pros Cons A Beginner’s Guide to Smart Investment Decisions A Closer Look at How to Build a Retirement Plan
Prospective buyers of variable annuities ought to recognize and take into consideration the financial problem of the releasing insurance coverage company prior to getting in right into an annuity agreement. While the advantages and disadvantages of various kinds of annuities can be questioned, the actual concern bordering annuities is that of viability.
Nevertheless, as the stating goes: "Purchaser beware!" This short article is prepared by Pekin Hardy Strauss, Inc. ("Pekin Hardy," dba Pekin Hardy Strauss Wealth Monitoring) for informational functions only and is not intended as a deal or solicitation for company. The details and data in this article does not comprise lawful, tax obligation, audit, financial investment, or other professional advice.
Table of Contents
Latest Posts
Analyzing Annuity Fixed Vs Variable Everything You Need to Know About Financial Strategies Defining Variable Annuity Vs Fixed Annuity Advantages and Disadvantages of Fixed Indexed Annuity Vs Market-va
Decoding Tax Benefits Of Fixed Vs Variable Annuities A Comprehensive Guide to Investment Choices What Is Fixed Vs Variable Annuity? Features of Smart Investment Choices Why Fixed Annuity Vs Equity-lin
Highlighting the Key Features of Long-Term Investments Key Insights on Variable Vs Fixed Annuity What Is the Best Retirement Option? Benefits of Fixed Income Annuity Vs Variable Growth Annuity Why Cho
More
Latest Posts